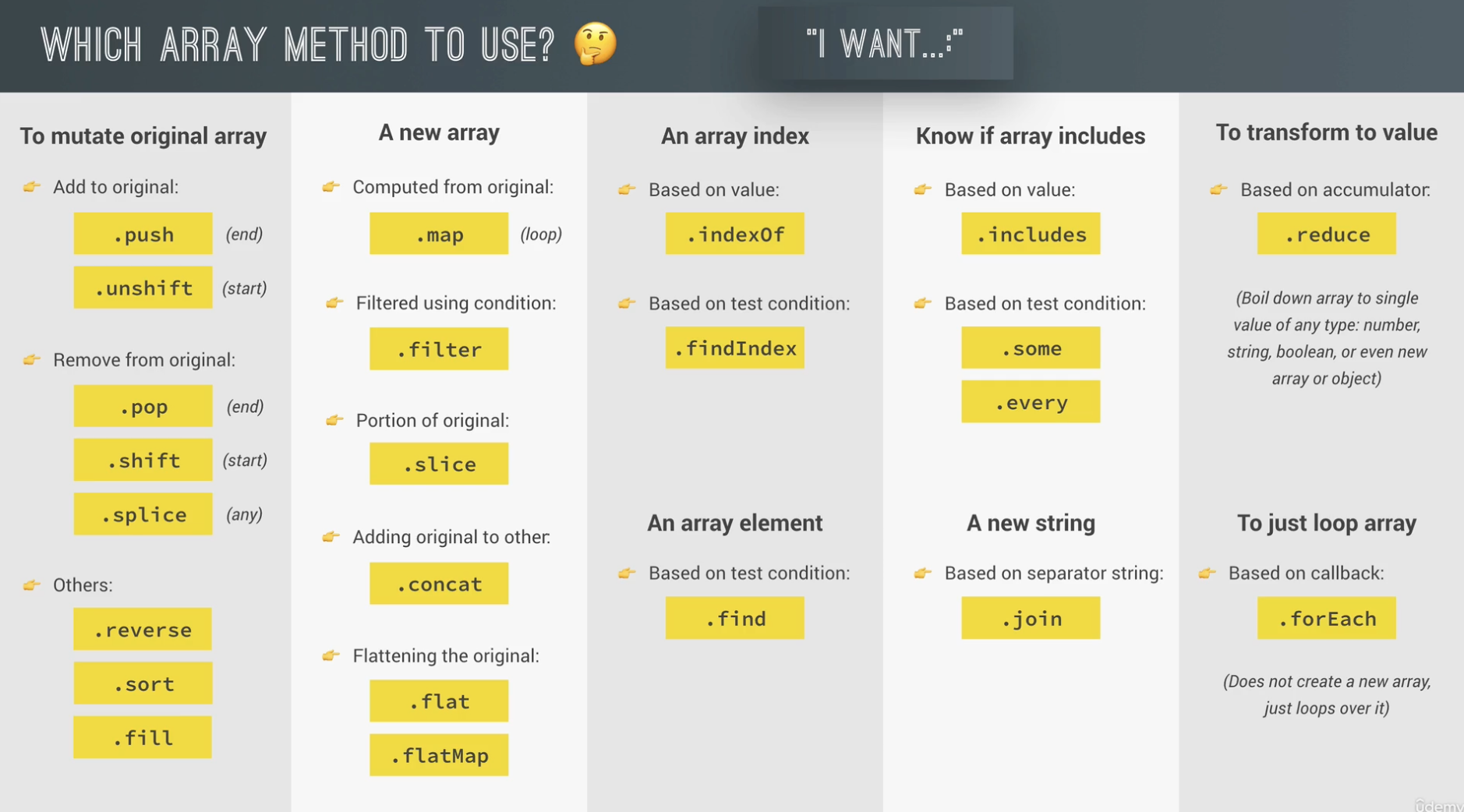
JavaScript 中的数组
创建数组的方式
简单方式:
js
console.log([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(new Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]编程方式:
js
const x = new Array(5);
console.log(x); // [空属性 × 5]
x.fill(5);
console.log(x); // [5, 5, 5, 5, 5]js
const x = new Array(5);
x.fill(5, 3); // 第二个参数制定从哪里开始
console.log(x); // [空属性 × 3, 5, 5]Array.from() :
js
const y = Array.from({length: 5}, () => 1);
console.log(y); // [1, 1, 1, 1, 1]js
const z = Array.from({length: 5}, (_, i) => (i + 1) * 1);
console.log(z); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]上方代码中的 _ 表示一个占位符,在代码中用不到,那个位置上仍然需要。
js
let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];slice() 提取数组的一部份
该方法不改变原数组。
js
console.log(arr.slice(2, 3)); // ['c']
console.log(arr.slice(2)); // ['c', 'd', 'e']
console.log(arr.slice(-2)); // ['d', 'e']
console.log(arr.slice(-1)); // ['e']
console.log(arr.slice(1, -2)); // ['b', 'c']使用 slice() 方法也可以获得数组的浅拷贝。
concat() 连接两个数组
(不改变原数组):concat()
js
let nums = [1, 2];
const letterAndNum = arr.concat(nums);
console.log(letterAndNum); // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 1, 2]
console.log([...arr, ...nums]); // ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 1, 2]join() 将数组元素连接为字符串
(不改变原数组):join()
js
console.log(arr.join(' - ')); // a - b - c - d - eat() 查询数组元素
除了方框之外,可以使用 at() 方法:
js
let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'];
console.log(arr.at(-1)); // e
console.log(arr[arr.length - 1]); // e遍历数组
for ... of
js
for (const item of arr) {
console.log(item);
}
for (const [index, item] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(index, item);
}forEach()
js
arr.forEach((item, index, array) => {
console.log(index, item);
});map(), filter(), reduce() 从其他数组中获取新数组
map(): 映射原数组,通过回调函数对原数组中的每个元素都执行相同的操作,最终返回执行操作后的值。
js
const movements = [200, 450, -400, 3000, -650, -130, 70, 1300];
console.log(movements.map(item => item * 2)); // [400, 900, -800, 6000, -1300, -260, 140, 2600]filter(): 过滤原数组,返回满足条件的元素构成的数组。
js
console.log(movements.filter((value, idnex, arr) => value < 0)); // [-400, -650, -130]reduce(): 将所有元素通过一定操作最终合为一个,比如连加连乘等等,想象一下“雪球效应”。
js
console.log(movements.reduce((pre, cur, curIndex, arr) => pre + cur)); // 3840find() 返回第一个满足条件的元素
js
const movements = [200, 450, -400, 3000, -650, -130, 70, 1300];
console.log(movements.find(mov => mov < 0)); // -400当一个数组中有多个对象的时候,可以利用这个强大的特性寻找其中某个对象:
js
console.log(accounts.find(acc => acc.owner === 'Jonas Schmedtmann')); // {owner: 'Jonas Schmedtmann', movements: Array(8), interestRate: 1.2, pin: 1111}findIndex() 返回第一个满足条件的元素的索引
js
const movements = [200, 450, -400, 3000, -650, -130, 70, 1300];
console.log(movements.findIndex(mov => mov < 0)); // 2includes() 检查数组中是否有某个元素
js
console.log(movements.includes(100)); // flasesome() 检查数组中是否有包含某个条件的元素
js
console.log(movements.some(mov => mov < 0)); // trueevery() 检查数组中是否所有元素都满足一定条件
js
console.log(movements.every(mov => mov < 0)); // falsesplice() 删除/添加元素
该方法改变原数组。
语法:
splice(start)
splice(start, deleteCount)
splice(start, deleteCount, item1)
splice(start, deleteCount, item1, item2)
splice(start, deleteCount, item1, item2, /* …, */ itemN)返回值:一个包含了删除元素的数组,如果没有删除元素就返回空数组。
例子:
js
console.log(arr.splice(2)); // ['c', 'd', 'e'] 删除的元素
console.log(arr); // ['a', 'b'] 剩下的元素
console.log(arr.splice(-1)); // ['b'] 删除的元素
console.log(arr); // ['a'] 剩下的元素js
console.log(arr.splice(2, 2)); // ['c', 'd'] 删除的元素
console.log(arr); // ['a', 'b', 'e'] 剩下的元素reverse() 数组逆序
(改变原数组):reverse()
js
console.log(arr.reverse()); // ['e', 'd', 'c', 'b', 'a']
console.log(arr); // ['e', 'd', 'c', 'b', 'a'] 原数组发生了变化flat(n) 打平第 n 层数组
js
const arr = [[1,2,[3]],[4,5,6],7,8];
console.log(arr.flat()); // [1, 2, [3], 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
console.log(arr.flat(2)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]数组排序
sort() 函数会改变原数组。
字符串排序:
js
const owners = ['jonas', 'zach', 'adam'];
const sorted = owners.sort();
console.log(sorted); //['adam', 'jonas', 'zach']数字排序:
js
const movements = [200, 450, -400, 3000, -650, -130, 70, 1300];
console.log(movements.sort()); // [-130, -400, -650, 1300, 200, 3000, 450, 70]
// 注意上面的排序并不是按照大小,而是按照字符的 assci 前后顺序按数字大小排序:
js
console.log(movements.sort((a, b) => a - b)); // [-650, -400, -130, 70, 200, 450, 1300, 3000]