第一节课
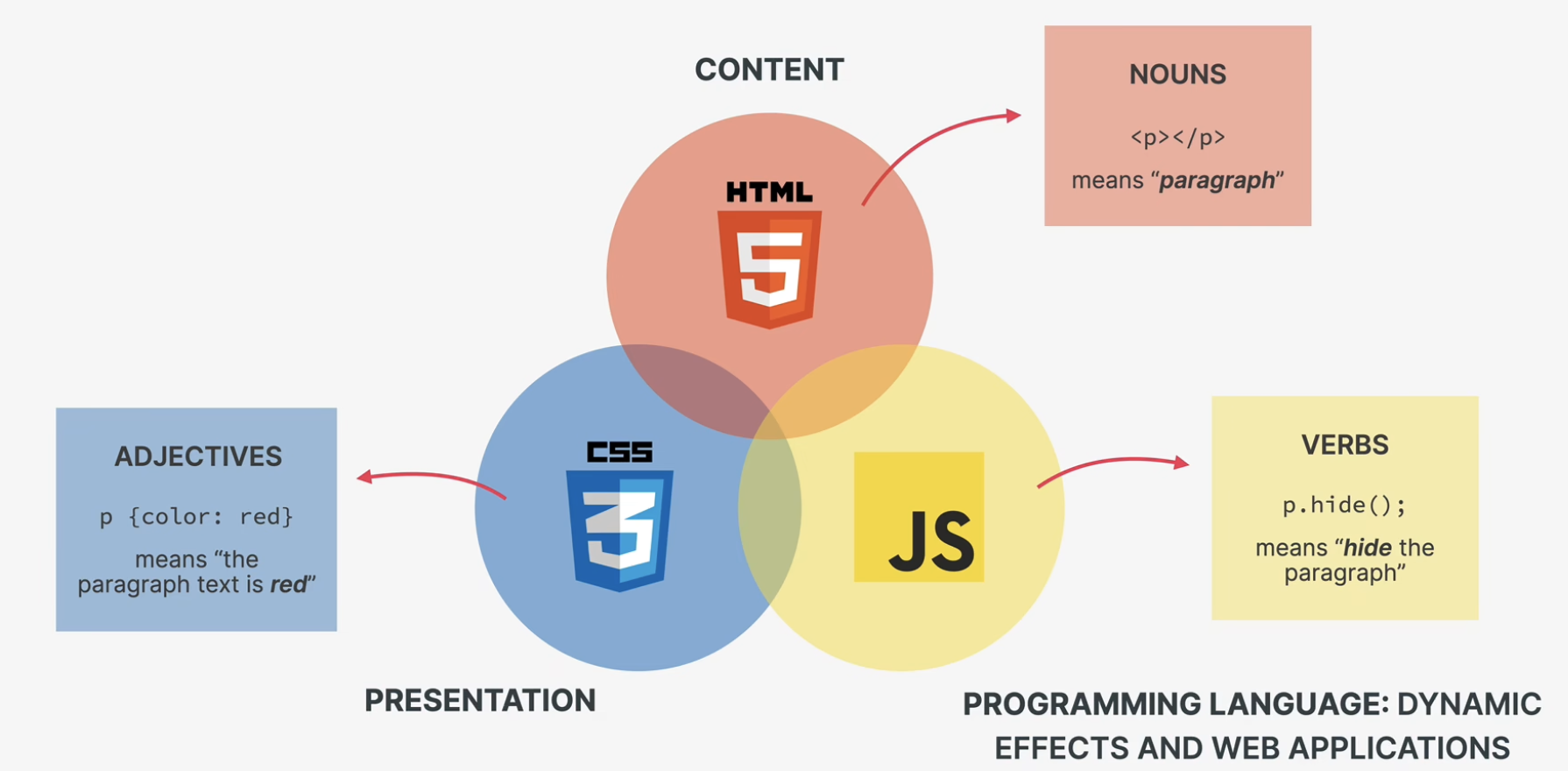
语义化 HTML
例如,不用 <b></b> 而用 <strong></strong> 来加粗。这种语义化标签是在 HTML5 中被引入的,它和 div 并没有什么本质上的区别,只是名字不同,那么它的好处是什么呢?
- 搜索引擎优化,让搜索引擎能够理解结构并且更好地分析。
- 可访问性更好,尤其是对于依靠屏幕阅读器阅读网页的人群。
- 可读性更好。
- 编写更容易。
CSS 基础
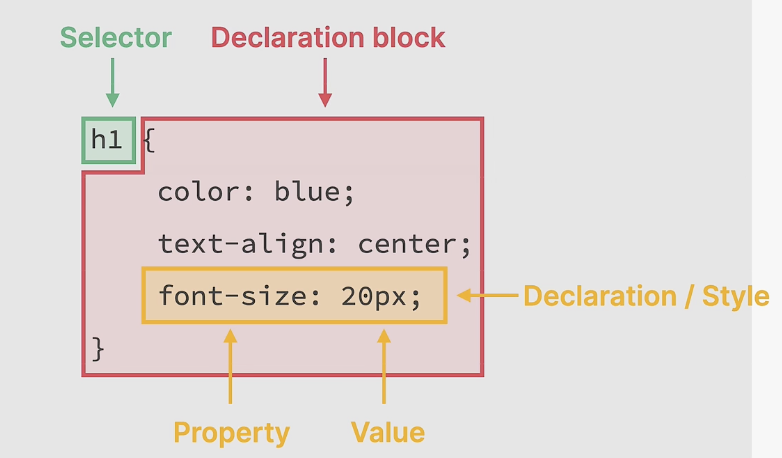
一个常见的 CSS 代码快包括:选择器、属性、值。
CSS 主要有三种类型:
- 内联 CSS (inline),尽量不要使用🙅♀️。
- 内部 CSS (internal),使用
style标签。 - 外部 CSS (external),使用
link连接。
设置文本的基本属性
css
h1 {
font-size: 26px; // [!code highlight]
font-family: sans-serif; // [!code highlight]
text-transform: uppercase; // [!code highlight]
font-style: italic; // [!code highlight]
}
p {
font-size: 22px;
font-family: sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5; // [!code highlight]
}
h4 {
font-size: 20px;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-align: center; // [!code highlight]
}组合选择
列表选择器
使用逗号隔开,选择列表中的所有元素:
css
h1,
h2,
h3,
h4,
p,
li {
font-family: sans-serif;
}后代选择器
使用空格隔开,选择前面那个元素(父元素)的子元素:
css
footer p {
font-size: 16px;
}id 选择器
用 # 选择一个具体的元素:
js
#author {
font-style: italic;
}id 是唯一的,不允许重复命名,一个 id 只能分配给一个元素。但写代码的时候尽量不要使用 id🙅♀️ ,这可以为未来做好准备。
class 选择器
css
.related-author {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
}伪类
一个冒号后面接相应的修饰词用于选择相应的元素。
js
li:first-child {
font-weight: bold;
}上面的代码中所做的操作是选择了所有 li 元素中的第一个元素。
js
li:nth-child(2) {
color: red;
}选择所有 li 元素中的第二个元素。
js
li:nth-child(odd) {
color: red;
}选择所有 li 元素中的第奇数个元素。
改变链接🔗的样式,改变元素颜色并去除下划线:
js
a:link {
color: #1098ad;
text-decoration: none;
}鼠标悬浮:
js
a:hover {
color: #e65714;
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: underline dotted;
}